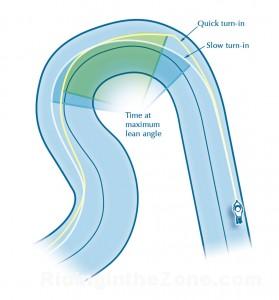
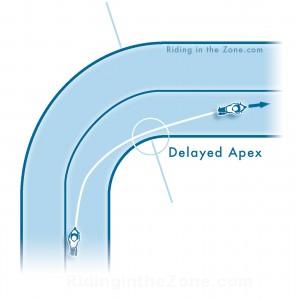
Hot on the heels of the The Power of the Quick Turn article is this followup post about what happens after you tip into a corner. Too many riders struggle with cornering, not necessarily because they are afraid to lean, but becasue they do not understand how to properly complete a turn.
Cornering Basics
By now you know that motorcycles must lean to change direction and that leaning is done by countersteering. Read about countersteering HERE.
Once the bike begins to lean, countersteering pressure is reduced and other dynamics take over that cause the motorcycle to arc around the curve, including front end rake and trail geometry, as well as something called camber thrust. Camber thrust is the term that describes how a tapered object (a motorcycle tire leaned over) orbits around its axis when rolling along a surface (the pavement).
In other words, the rounded profile of a motorcycle tire acts like a tapered styrofoam cup when it’s rolled on its side. Give it a push and it rolls in a circle.
Here is how author and fellow USCRA racer Tony Foale describes camber thrust:
“As the inside edge of the tyre is forced to adopt a smaller radius than the outer edge, then for a given wheel rotational speed, the inner edge would prefer to travel at a smaller road speed, this happens if the wheel is allowed to turn about a vertical axis through the point of the cone. Just as a solid cone on a table if given a push.”
For our purposes, all you really need to understand is that your motorcycle is designed to track around a curve with minimal effort once the bike is in a lean. Front end geometry (caster effect, rake, trail, etc.) all make this possible. If you want to read more, go to Tony Foale’s website and learn all about it.
If your bike is properly maintained and has relatively new tires with nearly the original profile intact, you should be able to initiate lean and then maintain that lean angle without introducing any significant handlebar inputs. Problems occur when the rider messes this process up. Most bikes will track predictably and with little effort as long as the rider doesn’t interfere with the process or introduce counterproductive inputs.
Variations in Machine Design
Some riders insist that they cannot round a corner without using significant handlebar pressure to keep their machine on the desired path. Instead of being able to relax and let the bike carve the path, they fight the bars all the way around the curve. It is possible that the machine is to blame, but these days this is rarely true.
While I have ridden bikes with really bad cornering dynamics, the vast majority of modern machines offer balanced, neutral handling that requires little-to-no mid-corner intervention. The only reason for handlebar adjustments are because of mid-corner changes in turn radius, camber or surface condition. A smooth constant radius curve, ridden well, requires almost no additional handlebar pressure.
It’s important to note that different types of bikes handle differently. Sportbikes are responsive to steering inputs, while cruisers tend to be slower steering, but more stable. Still, if the rider does all the right things, then the differences in machine does not make that much of a difference. The trick is to have the knowledge and skill to complete a corner proficiently.
Basically, it’s usually much more productive to evaluate the user instead of blaming the machine.
User Error
To repeat…once the necessary lean angle is established, most bikes are happy to track around a corner with little effort. So, why do some riders struggle with this part of the cornering process? The answer lies in a few areas.
- Tension at the handlebars. The front of the bike needs to be free to move up, down, and side -to-side in response to both large and small changes in the road surface. Being stiff on the handlebars interferes with this motion and causes the motorcycle to feel reluctant to turn. It also asks the tires to work harder to stay in contact with the surface. Another problem with stiff arms is that you are inhibiting the slight countersteering corrections that may need to occur to deal with changes in camber or other variations in corner surface. Loose arms allow fluid reactions.
- Poor body position. Think of your bike as your dance partner who wants you to lead. In the case of the cornering dance, a slight dip of the shoulder to the inside of the curve will encourage smoother cornering. In contrast, a rider who stays upright or leans outside is stepping on the bike’s toes, causing it resist fluid cornering.
- Not using the Throttle Correctly. For the motorcycle to track around the corner predictably and smoothly, the suspension must be stable and in the middle of its travel. Smooth, gradual acceleration throughout the curve produces the best results. Be sure to slow enough at the beginning of turns so that you can comfortably roll on the gas all the way to the exit. Unfortunately, a lot of riders fail to use steady throttle in corners. This is a problem, because changes in speed and drive force alter the arcing path the motorcycle takes. Abruptly chopping on or off the throttle upsets this stability and causes the bike to lift and fall in and out of the established angle of lean and introduces forces that result in a wobbly or weaving line around the corner. Note that acceleration typically makes the bike drift wide and deceleration can either cause the bike to drop into the corner more or cause it to stand up, depending on how abruptly the throttle is chopped and how the machine /tire combo responds to this input.
- Not Looking through the Turn. You tend to go where you look, so look where you want to go! By keeping your visual attention through the turn and toward the corner exit, your mind is able to better manage the corner. The other advantage is that the landscape slows down when you look ahead. This reduces anxiety and helps complete the concerning process. Looking ahead will not suddenly make you a cornering master, but without habitually looking ahead, you will never become one. Keep your eyes up.

Cornering Technique
Okay, so let’s break it down.
- Look well ahead.
- Countersteer to initiate lean for the corner.
- Crack the throttle as soon as the bike is leaned. Use gentle drive at first and then progressively feed in more drive force. Roll on with more authority as lean angle is reduced near the corner exit. Steady drive creates steady cornering.
- Relax! If you established the correct angle of lean for the turn, the bike should require only slight adjustments in handlebar pressure. Corners that tighten will require you to press more on the inside bar to lean the bike more, but keep the throttle as steady as possible.
- Finish the turn. You’re not done yet. Keep looking toward the corner exit and roll on the throttle a bit more to let the bike drift toward the outside of the curve. This facilitates the “outside-inside-outside” cornering line, which I will discuss in a future post.
- Rinse and repeat for the next corner.
There is so much more to learn about the cornering process, but this is a good start. Implement these steps and you’re well on your way to becoming a cornering master.
What tips can you share that help you to corner with more confidence?
Please Donate to Keep the Articles Coming
If you liked this article and the many other articles on this site, please toss a buck or five into the hat. It’s greatly appreciated!
- Click the PayPal “Pay Now” button.
- Then indicate quantity in $2.00 increments. – Example: put “2” in “QUANTITY” field to donate $4.00, “3” for a $6.00 donation, etc.
Why $2.00? Due to the PayPal fee structure, a $2.00 donation is significantly more beneficial compared to a $1.00 donation.
Thank You!
Check out these related posts:
- The Power of the Quick Turn
- Just Go Faster
- Countersteering Will Save Your Life!
- The “No Countersteering” Myth
- Valuing Motorcycling Skill Development
- #1 Reason for Motorcycle Crashes in Corners